2-Bromopropionic Acid: Depth Commentary on a Chemical’s Journey and Promise
Historical Development
Looking back at the roots of 2-bromopropionic acid takes us into the century-old landscape of organic chemistry, where scientists kept testing out halogenation reactions to expand the boundaries of acid derivatives. Early synthetic chemists found bromopropionic acids through direct bromination of propionic acid, following the spirit of discovery from the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Interest picked up once folks realized the compound’s potential as a versatile intermediate in pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals, especially once substitution chemistry became a well-worn path in research labs. Over the years, changes in industrial processes and access to better purification have allowed for more controlled production, which has supported the compound’s steady integration into research and production pipelines. This journey reflects the push to wring every bit of usefulness from simple molecular scaffolds, with 2-bromopropionic acid serving as a case study in making the most of small chemical tweaks.
Product Overview
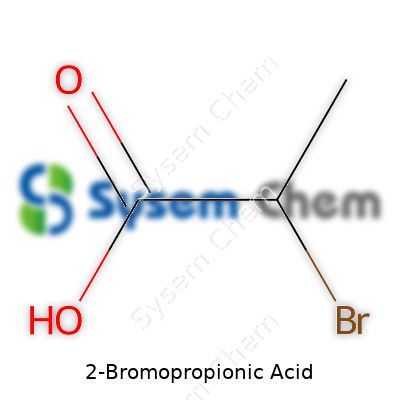
2-Bromopropionic acid stands out in the chemical world due to its unique bromo-carboxylic configuration. This modest three-carbon acid, sporting a bromine atom on the alpha carbon, sets itself up as a building block for everything from custom drug molecules to intermediates for advanced polymer production. In the day-to-day operations of laboratories, its reputation comes from how often it slides into synthetic schemes as a stepping stone, helping chemists add complexity or functional groups to target molecules. Modern manufacturers make sure that bottles of this acid are consistently pure, keeping the bench scientist’s experience as frustration-free as possible, which matters during tricky synthetic sequences where one impurity can derail a month of work.
Physical & Chemical Properties
Seeing 2-bromopropionic acid freshly distilled, you’d notice a colorless to faintly yellow liquid, solidifying near room temperature, depending on its purity and storage. Its melting point clocks in near 47°C and boiling creeps up close to 210°C, letting it straddle the edge between liquid and solid in many environments. The acid shows clear solubility in water and a whole spectrum of organic solvents, which makes it handy for both aqueous and organic phase reactions. The molecule packs some punch with acidity (pKa hovering just above 2.5), meaning it can donate protons in numerous catalytic settings—this property brings special attention in esterification or amidation workflows. The alpha-bromo position marks it as reactive, ready to undergo nucleophilic substitutions or eliminations, and gives chemists multiple avenues for adding more complexity to their synthetic strategy.
Technical Specifications & Labeling
On the technical front, most bottles you’ll find in academic or industrial stockrooms declare at least 98% purity, sometimes nudging past 99% for pharmaceutical purposes. Impurities mostly track to unreacted propionic acid, traces of dibromides, or hydrolysis byproducts. Each label ought to show a proper chemical abstract number, molecular weight (which stands at 151.98 g/mol), and standardized storage instructions—avoiding moisture and bright light, all to safeguard the acid’s lifespan. Good suppliers also flag transport hazard codes since this acid sits in the irritant class and demands specific packaging under international chemistry trade rules. Expiry dates may seem cautious, but they keep attention on freshness, as brominated acids sometimes age faster than their plain cousins.
Preparation Method
The most common lab preparation approach involves gradual bromination of propionic acid under controlled temperature in the presence of phosphorus catalyst or red phosphorus. Careful chemists keep a close eye on both temperature and mixing, because the chance of over-bromination looms when things run too hot or out of balance. After the reaction, distillation separates the desired acid from side-products. Some routes favor sodium bromide and sulfuric acid in a mixed batch, especially for scale-ups in industry, where high yield matters. These methods echo decades of tinkering with both cost and yield—modern practitioners still favor the direct route, thanks to manageable hazards and decent selectivity, while advanced settings sometimes try greener alternatives, hoping to swap out hazardous reagents for more sustainable ones.
Chemical Reactions & Modifications
Ask any organic chemist, and you’ll hear a medley of stories about using 2-bromopropionic acid for fine-tuned chemical reactions. Its alpha bromine lures nucleophiles like amines or thiols, letting one swap the bromine out for nearly any group you need. Decarboxylation, halogen exchange, and coupling reactions spin from the same starting acid. Its value keeps popping up in pharmaceutical chemistry, where the acid anchors chiral auxiliaries for asymmetric synthesis or helps make unusual amino acid derivatives for peptide research. Side chain elaboration, ester formation, and amidation are popular follow-ups, especially for custom molecules in labs driven by curiosity or commercial needs. These characteristics keep 2-bromopropionic acid nestled firmly on the foundation chart of synthetic organic chemistry.
Synonyms & Product Names
Searching through catalogs and scientific reports, you’ll spot this compound under several guises: alpha-Bromopropionic acid, 2-BP, 2-Propanebromonic acid, and its robust CAS registration, 598-72-1. Multilingual suppliers sometimes label it as Acido 2-bromopropionico or 2-brompropionsäure. These aliases pop up in everything from technical data sheets to global customs documents, so a clear grasp of the lingo saves a lot of searching and miscommunication. Familiarity with its alternate spellings also helps importers and compliance officers avoid paperwork nightmares.
Safety & Operational Standards
Handling 2-bromopropionic acid is a routine task for experienced lab techs, but no one treats it lightly. Splashes on skin or eyes cause strong irritation, driven by both acidity and halogen reactivity. Vapor exposure irritates the nose and throat fast. Good lab hygiene—gloves, goggles, and solid ventilation—goes from habit to necessity here. Accidental spills demand neutralization with sodium bicarbonate, never water alone, since mixing with water can sometimes generate heat and fumes. Storage far from oxidizers or bases proves key, and up-to-date safety data sheets guide everyone from bench staff to shipping clerks on correct procedures. Waste streams can’t go down regular drains either; specialized incineration or chemical neutralization protects both people and soil.
Application Area
Fields that rely on 2-bromopropionic acid span further than the undergraduate teaching lab. Pharmaceutical groups draft it into blueprints for anticonvulsants and cardiovascular drugs, where its alpha-bromo handle spawns all sorts of side chains and structural backbones in active ingredients. Pesticide developers bank on it to modify crop protectants or fine-tune herbicides for better selectivity. Polymers and coatings gain fresh chemical handles by grafting derivatives made from this acid, with past uses in specialty plastics that stand up under extreme conditions. Research teams often see it as a go-to molecule for customizing peptides or making radiolabelled agents for imaging, since the bromine attaches easily to radioactive isotopes. A day in a busy R&D firm will often uncover no less than three ongoing projects tracing back to this single humble acid.
Research & Development
Money and time invested in R&D around 2-bromopropionic acid reflect both long-standing faith in halogenated intermediates and new ideas about expanded end uses. Recent years have shown research devoted to greener bromination methods and chiral resolution, often trying to streamline the process or reduce environmental load. Scientists also look at ways to use 2-bromopropionic acid in targeted drug design, especially where unusual side chains unlock binding in stubborn protein targets. There’s ongoing exploration into using this acid as a linker for polymer grafting, especially in bio-related coatings and smart hydrogels. The constant back-and-forth between synthetic ambition and cautious safety review means innovation arrives slowly, but with solid science guiding safer and more efficient practice in each new patent or publication.
Toxicity Research
Clear understanding of toxicity ranks high in the risk assessment of any halogenated acid, and 2-bromopropionic acid poses risks both in acute and chronic exposures. Inhalation or ingestion can damage mucous membranes, respiratory tract, and cause gastrointestinal upset. Animal testing indicates that the bromine group increases both target-organ toxicity and environmental persistence compared to plain propionic acid. Absorption through the skin raises concern, especially if proper protection lapses. Long-term lab animal studies point to nerve and liver stress at repeated, higher exposures, so regulatory agencies recommend stringent training for all staff. Newer toxicity screening aims to fill gaps on metabolic breakdown, since byproducts may also pose risks to aquatic life or accumulate in food chains, underscoring the need for careful stewardship and proper disposal.
Future Prospects
The next decade may very well see 2-bromopropionic acid step out of its supporting role in the chemical world. Sustainable synthesis and big advances in recycling brominated waste find support from digital planning tools, which help chemists predict greener paths and lower-risk procedures. In the biomedical sector, this acid may carve a place in custom prosthetics and imaging agents, while advances in catalysis could unlock new transformations once stymied by reactivity issues. Tightening health and environmental controls spur companies to design safer workflows and alternative packaging, pointing toward a future where efficient, responsible, and innovative use defines progress. If you spend enough time in research or small-scale manufacturing, you’ll keep running into 2-bromopropionic acid—often right at the nexus of challenge and possibility, a true workhorse for the next generation of scientific solutions.
Getting Familiar With 2-Bromopropionic Acid
The chemical formula for 2-bromopropionic acid comes down to C3H5BrO2. This compound might sound niche if you haven’t worked much in chemistry, biochemistry, or pharmaceuticals. Yet, the not-so-glamorous world of small molecules like this actually fuels a lot of medical and research progress. Sitting behind those characters lies the backbone of more lab work than you'd guess — and plenty of potential for innovation.
Why Does This Formula Matter?
Think about what happens in a university lab. Researchers need to synthesize molecules that mimic natural protons in proteins, design experiments for pharmaceutical candidates, or study enzyme reactions. 2-Bromopropionic acid serves as a building block or a probe in these fields. The specific arrangement of atoms matters because a change in the formula changes its behavior completely.
The bromine atom offers a unique handle. Swapping hydrogen for a bromine on a propionic acid changes both its reactivity and its path in metabolic experiments. That’s what gets researchers interested. If you’re developing better pain meds or new plastics, that C3H5BrO2 backbone turns up in your paperwork more than you’d expect.
Safety and Handling: Reality Check
In my early lab days, I got a quick lesson in why formulas aren’t just textbook answers. The bromine atom in 2-bromopropionic acid isn’t just for show. It brings some real hazards to the bench. The compound’s formula signals more than structure; it flags risks. 2-bromopropionic acid causes burns and raises health concerns on skin contact or inhalation. You skip the gloves or goggles at your own risk. The chemical isn’t just another bottle on the shelf — treat it with respect, unless you want a call to campus health services.
Lab work gets safer if people actually read the formula and know what it stands for. Those numbers mean something when trying not to miscalculate dosages or mislabel waste. It’s easy to overlook, but a mistake in the formula leads to trouble. I’ve worked with new students who confused 2-bromopropionic acid with its parent propionic acid, only to find their reaction went sideways. Chemical literacy saves money and time, but most importantly, it keeps people safe.
From Academic Use to Industry Impact
Even outside research, C3H5BrO2 shows up. Agrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and material science firms might use it to modify other molecules, create more reactive intermediates, or tweak the function of polymers. Demand for specialty chemicals like this often sneaks up because new uses get published every year. For example, as a chirality source, this acid supports the production of cutting-edge drugs or biologically active molecules.
Solutions: Knowledge and Best Practices
If you’re keeping safety tight and accuracy high — both in industry and academia — share more about formulas like C3H5BrO2. Training sessions, clear signage, and accessible material safety data sheets help. Lab managers should push for more hands-on training. In my career, encouraging chemists to keep reference tables nearby had a measurable effect. Less confusion, fewer incidents, stronger results.
The chemical formula for 2-bromopropionic acid isn’t just for exams or databases. It connects to real-world health, industry success, and progress in science. Behind every scientific breakthrough sits the unflashy, often overlooked work of knowing your molecules inside-out.
The Chemical at a Glance
2-Bromopropionic acid stands out for its unique chemical structure—one bromine atom hanging off a short, three-carbon acid chain. This design turns it into a prime building block for labs and industries that demand accuracy. Whether you’re flipping through organic chemistry textbooks or diving into pharmaceutical research, this molecule keeps showing up.
Making Complex Molecules Simpler
In synthetic organic chemistry, 2-bromopropionic acid helps create more complicated compounds. Picture graduate students racing down the hall for reagent bottles. Labs mix this compound into reactions to tack on short, reactive chains. These chains, with a bromine atom, make it possible to swap out the bromine for another group. That technique powers up the toolkit for making new drugs, sweetening flavor chemicals, or preparing agents for electronic materials.
Building Chiral Centers for Pharmaceuticals
Pharmaceutical chemists face a tough job when designing drugs that fit snugly into biological pockets. A major part of drug creation relies on chiral molecules—the left-handed or right-handed versions. 2-Bromopropionic acid serves as a starting material for producing these chiral intermediates. Drug makers reach for it while building up antiviral medications, anti-cancer treatments, or even common painkillers. By tweaking 2-bromopropionic acid's structure, companies can deliver medicines that work better and come with fewer side effects. As more pharmaceuticals target very narrow biological signals, small intermediates like this one have only become more valuable.
Stepping Stones in Material Science
Materials science research benefits from this compound too. New polymers, smart coatings, and high-performance adhesives sometimes trace their roots back to a 2-bromopropionic acid backbone. As folks race to develop lighter and tougher materials for smartphones, cars, and even solar panels, compounds like 2-bromopropionic acid let researchers stitch atoms together in just the right pattern. I remember watching the look on a graduate student’s face after their model worked, producing a flexible but heat-resistant sheet—2-bromopropionic acid often part of the secret sauce.
Biochemistry: More Than Just a Building Block
Research teams in biochemistry use 2-bromopropionic acid not just as a tool for construction but as a way to study human biology. Enzyme research, especially in fields like cancer or neurodegenerative diseases, depends on small molecules that can attach to specific amino acids. The reactive nature of the compound, with its bromine atom, means it can lock onto proteins and help scientists map out how our bodies react in disease. By isolating certain pathways or mimicking natural substrates, research makes leaps in understanding where things go wrong in a cell. Good lab habits and careful chemical handling make using compounds like this possible, despite their reactivity.
Safety Always Comes First
Working with 2-bromopropionic acid demands attention. Its brominated character makes it much more than an innocent white powder. Safety goggles and fume hoods become second nature, and seasoned lab techs keep spills in check with training and discipline. As regulations for hazardous chemicals tighten, it pays off for industries and universities to invest in green chemistry and safer alternatives, wherever practical. But for now, the compound keeps earning its place in research and manufacturing.
Understanding the Risks
Every lab technician or chemical worker has stories about close calls with dangerous substances. 2-Bromopropionic acid falls into the category of chemicals that don’t give second chances if treated casually. This compound comes with a toxic profile and causes immediate irritation on contact with the skin, eyes, and respiratory tract. For folks like me who’ve spent long hours in chemical storage rooms and labs, safety never feels like just a set of rules — it’s daily practice. Health data confirms that exposure causes significant harm; workers exposed to similar haloacetic acids have faced respiratory symptoms and chemical burns. So, nobody can afford to take shortcuts.
Smart Storage Strategies
Effective storage starts with location. Dedicated, well-ventilated chemical cabinets prove essential; air circulation prevents dangerous vapors from collecting. From experience, I know the shelves have to carry sturdy, leak-proof containers. Glass works best because it’s chemically compatible and keeps the acid stable. Tight lids prevent leaks or the slow escape of fumes, which can quietly damage lungs over time. I once saw a poorly sealed sample set off a sensor and trigger a full corridor evacuation. You never want your team in that situation.
Temperature matters. Keep the acid in a cool area away from heat sources or sunlight, since high temperatures spark decomposition and chemical reactions. Avoiding metal shelving reduces the risk of accidental corrosion or unforeseen reactions. The best labs set up clear signage: the hazard symbols warn everyone right away, cutting down on careless mistakes.
Personal Protection — No Compromises
Personal protective equipment protects lives, not just clothes. No one should even handle the bottle without chemical-resistant gloves, a lab coat, and face shields or safety goggles. Even a small splash can bring on weeks of recovery or a costly medical bill. The cough that lingers comes from one careless inhalation. I’ve met too many people who regretted skipping their mask for “just a quick task.” Proper fume hoods pull vapors away from your breathing zone. Labs that invest in quality fume hoods see far fewer workplace incidents.
Accidents and Emergency Planning
No matter how careful you feel, mistakes happen — nobody’s immune. Having an easy-to-reach eyewash station and a drench shower turns a serious accident into a quick washout, rather than a trip to the ER. Spill kits designed for corrosive acids should be nearby, not locked in storage. Any seasoned safety officer will tell you to review spill procedures during every monthly safety drill. Reading about chemical exposures in the news always sounds like someone else’s problem until it hits your bench.
Waste disposal keeps communities safe, too. Pouring 2-bromopropionic acid down the drain risks environmental harm because water treatment plants aren’t built to handle it. Instead, collecting waste in clearly labeled containers and following local guidelines protects both workers and neighbors.
Cultivating a Culture of Safety
Supervisors who lead by example and reward good practice create safer workspaces. I remember a manager who used to walk the floor after hours, checking that everything was stored correctly. Those small habits stick with people. Safety training only works if it’s regular, hands-on, and backed by a reasoned commitment from leadership. Well-informed staff make labs more productive and keep everyone safe from accidents that can haunt careers.
The lesson I learned over years is simple. Stay alert, use the right gear, and treat every bottle with the respect it demands. That’s how science moves forward — and people get home without injury.
Getting to Know 2-Bromopropionic Acid
2-Bromopropionic acid isn’t something most folks run across unless they spend their days mixing chemicals or studying organic reactions. Its job often lands in labs and chemical plants where it helps build other molecules for industries like pharmaceuticals or advanced materials. Having handled plenty of acids and reactive chemicals in lab settings, I understand why people might take a closer look at safety when it comes to compounds like this.
The Real Risks on the Bench
The key issue with 2-bromopropionic acid is that it combines the corrosive bite of carboxylic acids with the sneaky persistence of organic bromides. If even a small amount splashes on skin, you’ll feel irritation pretty quickly—redness, itching, and even burns in higher concentrations. Gloves matter a lot here, as well as a sturdy lab coat, since splashes can turn a regular workday into a real problem fast.
Breathing in fumes from this chemical is nobody’s idea of a good time either. Overexposure may lead to sore throats, headaches, or even coughing fits. Fume hoods or strong ventilation cut down on these risks. Inhalation is often overlooked with liquids, but this compound’s volatility begs for respect.
Accidental contact with eyes could cause serious pain and possible damage. Immediate rinsing is crucial if that ever happens. Emergency eyewash stations can make the difference between a close call and a permanent injury. After seeing what can go wrong—I've watched a colleague rush to a station with burning eyes once—quick action becomes second nature.
Fire and Environmental Trouble
There’s also fire to think about. Although 2-bromopropionic acid doesn’t flame up as easily as some other lab solvents, it can release toxic gases if caught in a blaze, including hydrogen bromide. These fumes should never be taken lightly. We always keep extinguishers rated for liquid fires handy, just in case.
Spills find their way into drains or ground if cleaners don’t pay attention. This acid, with its halogen component, can mess with aquatic life. At my last workplace, small spills triggered full response drills to keep runoff out of the plumbing. Cleaning with absorbent pads and properly labeled waste containers proved better than anything else we tried.
Tougher Than Ordinary Acids
2-Bromopropionic acid doesn’t just sting like vinegar. It attacks from two fronts: corrosive acid properties and the potential for toxic brominated byproducts. Brominated organics sometimes linger in the environment, resisting breakdown. Over years, you start to appreciate why even small habits—like double-checking that bottle caps are sealed—end up being big deals.
Practical Steps for Safety
Routine safety training lowers the odds of mistakes. Written procedures posted at every workstation and regular practice drills pay off over time. Whenever new folks joined our lab, one of the first lessons involved handling corrosives. Simple things—goggles, gloves, and clear labeling—built a culture where people watched out for themselves and others.
Waste disposal remains a challenge for many smaller labs. Collection bins should be marked for halogenated acids. Our team partnered with experienced waste haulers who understood what goes in each drum, reducing the risk of mixing incompatible chemicals.
Looking Forward
Advances in chemical engineering may one day produce safer alternatives or ways to neutralize these compounds before they leave the lab. Until then, it’s about solid habits, protective gear, and treating each container like it’s got a surprise inside. No shortcut makes up for paying attention and keeping respect for what you’re handling.
Purity in the Real World of Labs and Factories
Anyone who has handled 2-Bromopropionic Acid can tell you how a chemical’s grade impacts both research results and industrial output. Skimping on purity interrupts reactions, wastes time, and can gum up pricey equipment. Most reputable suppliers set their targets high, and purity levels often reach 98% or above. For research or pharma projects where even minor contamination throws things off, grades bump up to 99% or more. It takes tight controls and careful handling to keep these standards real and consistent.
Store shelves in university labs often see clear labeling stating “98%” or “99%” right on the bottles. Analytical reports from suppliers back these numbers, showing GC or HPLC results for every lot. I’ve called sales reps myself, grilling them for the latest COA, because a batch just below spec can mean hours of troubleshooting later. That one or two percent of impurity can muck up a synthesis or feed unwanted byproducts into larger factory runs. These aren’t theoretical worries—they show up in the troubleshooting notes for failed experiments and in the maintenance logbooks at production plants.
Packaging Sizes: Why It’s Not One-Size-Fits-All
Packaging choices follow how people actually use the chemical. In academic settings, I’m used to seeing 25-gram or 100-gram glass bottles lined up in the storage cabinets. You hardly ever need more for your average research project. Factories order far larger amounts, so 500-gram, 1-kilogram, or even 5-kilogram packages become the standard. Bulk shipments stretch up to 20 or 25 kilograms in a drum. Each size serves its own routine, avoiding waste and staying in budget.
There’s logic behind every lid and bottle. Glass stays popular at the bench, since the acid can chew through some plastics and doesn’t leach as much. In larger volumes, thick-walled plastic drums or steel containers arrive shrink-wrapped on pallets. I’ve watched a loading dock worker haul a blue drum across the floor, careful not to crack the outer layer because a spill triggers days of cleanup and paperwork. Small packs let researchers stay nimble; bulk containers keep manufacturing lines moving for days without disruption.
Safe Handling: Packaging’s Hidden Job
2-Bromopropionic Acid asks for respect. Acids in general bring risks to skin, eyes, and airways, and a good package prevents leaks and keeps vapors in check. Tamper-evident seals, sturdy lids, and warning labels turn out to be more than regulatory red tape—they keep people and workplaces safe. I remember unpacking a bottle and feeling grateful for the thick glass and airtight seal, especially after working in a shared lab where mistakes travel fast and accidents impact everyone.
Disposal rules also lean on packaging. Leftover bottles or drums end up as hazardous waste, and clear markings help facilities staff keep chemicals sorted for proper disposal. Sometimes labs pool leftovers into a single waste container labeled by hand, which doesn’t work nearly as well as the supplier’s marked drum from the start.
Room to Improve: The Road Ahead
Producers have room to rethink packaging for sustainability, too. Single-use plastics fill lab bins, and reducing pack size options or switching to recycled materials would help. More transparent reporting on actual tested purity, rather than only listing the minimum guarantee, would also spare users from surprise setbacks. Lab managers can ask suppliers upfront for more detailed batch data and eco-friendly packaging, speaking with their orders instead of just their complaints.
For anyone using 2-Bromopropionic Acid, knowing what to expect from purity and packaging isn’t a side concern—it’s the difference between smooth workflow and real headaches. In the end, those fine points shape discovery, productivity, and daily lab safety.